Biotics & the Skin Microbiome: How Probiotics, Prebiotics & Postbiotics are shaping the future of Dermatology
05/12/2025 | Probiotherapy | 10 min read

"Biotics are no longer a trend — they are the scientific foundation for a new generation of dermatological strategies that restore balance, not destroy it."
At YUN Probiotherapy, we use live probiotics, targeted pre- & postbiotics, and microbiome-safe formulations to support skin health without disturbing the skin’s natural ecosystem.
As microbiome science evolves, the terminology around probiotics, prebiotics, postbiotics, and synbiotics is becoming increasingly important—not only in nutrition, but in topical dermatology as well.
From acne- to atopic-prone and sensitive skin, we see how targeted biotics can help stabilize pH, support beneficial bacteria, and restore microbial balance in a gentle, evidence-based way.
In our new article, we explore:
- How each biotic category interacts with the skin microbiome
- Why microbiome-safe dermatology matters
- Opportunities for topical biotic therapies across key skin concerns
- How biotics enable a more precise, microbiome-based approach
Biotics are more than a trend. They are transforming how we understand and care for the skin. By integrating probiotics, prebiotics, postbiotics, and even synbiotics into dermatology, we move toward science that restores instead of disrupts—for now and for generations to come.
Why the Skin Microbiome matters
The skin microbiome is a dynamic ecosystem composed of billions of bacteria that interact constantly with the host. When this balance is disturbed, for example by hormonal changes, stress, medication, pollution, occlusion, or aggressive cosmetic ingredients, the microbial community can shift. Such imbalances can contribute to a wide range of concerns, including redness, blemish-prone skin, dryness, irritation, and discomfort in delicate areas. The microbiome is a key player in skin health, one that dermatology can no longer afford to overlook.
"Up to 90% of chronic eczema
lesions show microbial imbalance." *1
Our approach focuses on supporting the skin’s natural microbial balance with targeted biotics, rather than disrupting it.
Below is a table summarizing the four main biotic types, their effects, benefits, and limitations. This overview introduces the key concepts before we dive deeper into each biotic in the article.
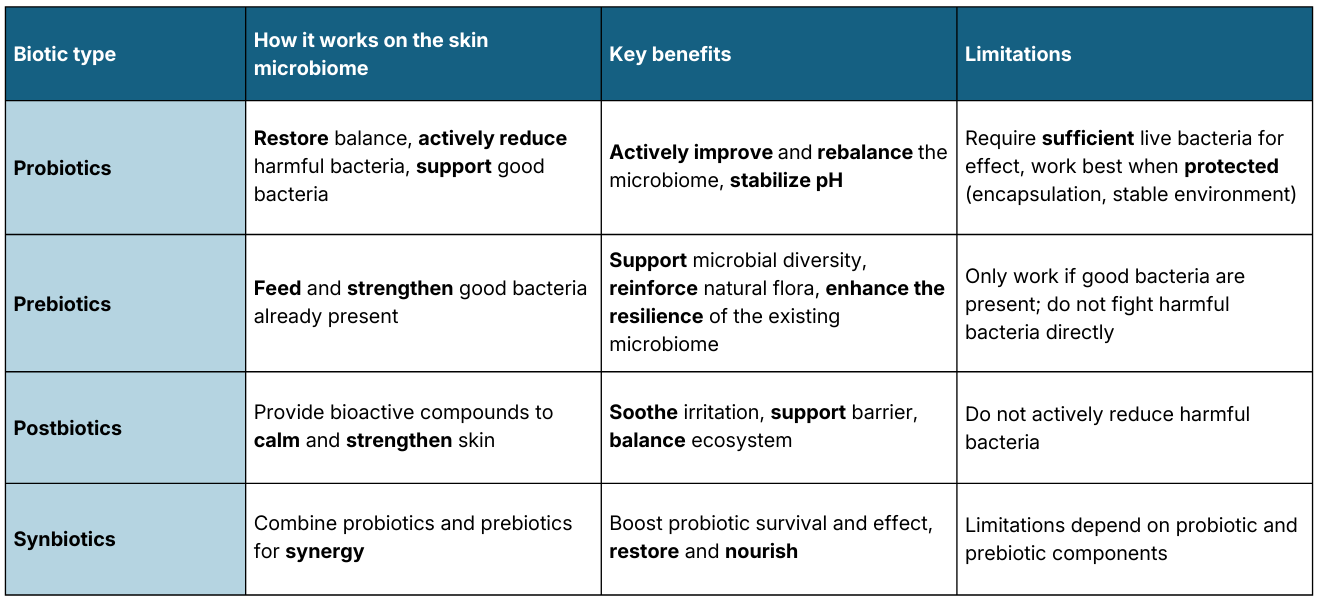
1. Probiotics
Probiotics are living microorganisms that, when applied in adequate (read ‘sufficient’) amounts, can exert a beneficial effect on the host. *2
YUN uses scientifically characterized Lactobacillus strains for topical use, including:
- Lactiplantibacillus pentosus YUN-V1.0
- Lactiplantibacillus plantarum YUN-V2.0
- Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus YUN-S1.0
These strains have been thoroughly documented by YUN for their ability to produce lactic acid and for their inhibitory activity against unwanted microorganisms, making them relevant for dermatological applications where microbial imbalance plays a role.
In topical applications, probiotics can:
- rebalance the skin microbiome
- support beneficial bacteria
- help stabilize pH
- counteract unwanted microorganisms
2. Prebiotics
Prebiotics are substrates that are selectively utilized by host microorganisms conferring a health benefit. *3
Applied topically, they help keep the skin’s microbiome stable by feeding the good bacteria that naturally live on your skin, while leaving the skin barrier intact.
YUN formulates with prebiotics such as inulin, fructooligosaccharides (FOS), and oat, which help support Lactobacillus growth without disrupting the skin barrier.
Prebiotics can:
- selectively feed beneficial skin bacteria (only if present)
- support microbial diversity
- strengthen natural flora
- preserve skin equilibrium
Prebiotics only feed beneficial bacteria if present. They help maintain and strengthen the good bacteria, but do not actively reduce harmful ones.
3. Postbiotics
Postbiotics are preparations of inanimate microorganisms and/or their components that confer a health benefit on the host. *4
Postbiotics are non-living, functional compounds produced by bacteria. Although they no longer contain viable organisms, they can offer significant biological activity on the skin. Examples include Lactococcus ferment lysate and Lactobacillus ferment lysate.
Postbiotics can:
- support and reinforce the skin barrier
- help soothe reactive or sensitized skin
- reduce visible signs of irritation
- contribute to a more balanced micro-ecosystem
Postbiotics cannot counteract unwanted microorganisms to the same level as probiotics. While postbiotics offer important benefits for barrier support and soothing the skin, they do not actively reduce harmful bacteria like probiotics do. Their main role is to reinforce and balance the skin ecosystem, rather than directly suppressing unwanted microbes.
4. Synbiotics
Synbiotics are combinations of live beneficial microorganisms (probiotics) and selective substrates that support their growth (prebiotics), designed to improve the survival, activity, and functional impact of the probiotic strains. This powerful duo helps probiotics survive and do their job even better on the skin.
On the skin, synbiotics can:
- enhance the efficacy of applied probiotics
- create a favorable environment for beneficial bacteria to thrive
- support better microbial balance after disruption (e.g. medication, hormones, stress)
- strengthen the resilience and diversity of the skin microbiome
- actively counteract unwanted bacteria through in situ competition and production of bioactive molecules (thanks to the probiotic component)
Synbiotics can actively reduce harmful bacteria, thanks to the probiotic part. This is what sets them apart from prebiotics and postbiotics, which do not fight harmful bacteria directly. Pre- and postbiotics are excellent for maintenance and soothing, but only live probiotics can actively outcompete pathogens.
“Pre- and postbiotics are excellent for maintenance and soothing, but only live probiotics can actively outcompete pathogens.”
The building blocks of YUN Probiotherapy™
YUN Probiotherapy™ brings together live probiotics, pre- and postbiotics, and microbiome-safe formulations, each carefully developed to repair, strengthen, and protect the microbiome. Together, they form a powerful, adaptive system that respects the body’s complexity and delivers sustainable, visible results.
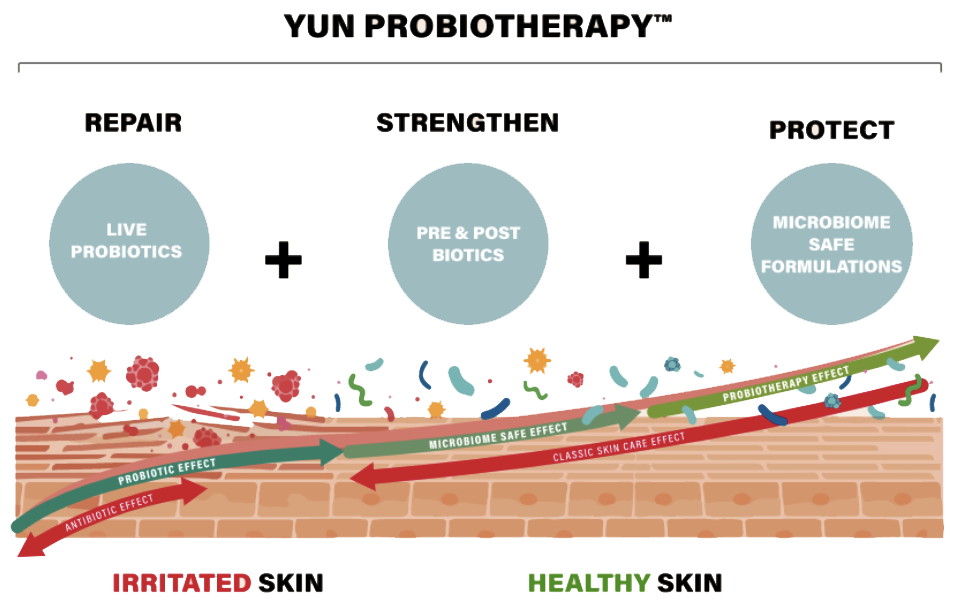
- Repair: Live probiotics help restore balance to irritated skin by actively supporting beneficial bacteria and reducing harmful ones.
- Strengthen: Pre- and postbiotics nourish and reinforce the skin’s microbiome, making it more resilient and comfortable.
- Protect: Microbiome-safe formulations maintain long-term skin health by preserving microbial diversity and preventing unnecessary disruption.
This approach bridges science and daily skincare, showing how targeted biotics work together for healthier skin from irritation to lasting balance.
Why Biotics matter for Dermatology
A growing body of evidence shows that the skin microbiome plays a key role in:
- barrier integrity and repair
- hydration and TEWL regulation
- pH balance and lipid metabolism
- innate immune responses
- sensitivity and reactivity
Biotics offer a microbiome-supportive approach that works with the natural microbial community rather than suppressing it. This results in targeted, gentle strategies that align with how the skin functions biologically.
At YUN, we believe in microbiome-compatible dermatology: formulations that respect microbial diversity, minimize unnecessary antimicrobial pressure, and support long-term skin health. This includes:
- microbiome-safe formulation principles
- targeted use of live probiotics where repair is needed
- maintenance with pre- and postbiotics
- long-term strategies that preserve microbial resilience
What this means for Dermatology Portfolios
For brand owners, formulators and dermatology portfolio leaders, biotics represent a shift in how skin health solutions are developed.
Instead of broad antimicrobial approaches that can disrupt the skin ecosystem, biotics enable microbiome safe, precision dermatology. This reduces the risk of irritation, improves tolerance and aligns with current regulatory and sustainability expectations.
YUN Probiotherapy™ is designed as a platform, not a single ingredient solution.
It combines live probiotics, targeted pre and postbiotics, and microbiome safe formulation principles into a modular system.
This platform allows brands to build coherent dermatology portfolios across multiple indications, including acne prone, sensitive and atopy prone skin, while working from one consistent scientific framework.
The result is dermatology that supports and protects the skin’s natural ecosystem instead of disrupting it.
Discover how YUN Probiotherapy™ can strengthen your dermatology portfolio.
References (short format)
- *1 Leyden et al. (1974) Microbial flora in atopic dermatitis lesions. British Journal of Dermatology. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/4601016/
- *2 Hill et al. (2014) ISAPP consensus on probiotics. https://www.nature.com/articles/nrgastro.2014.66
- *3 Gibson et al. (2017) ISAPP consensus on prebiotics.
- *4 Salminen et al. (2021) ISAPP consensus on postbiotics. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33948025
The future of health
is microbiome-safe
The industry is changing. Consumers demand safer, natural solutions and microbiome-safe care is becoming the new standard.
At YUN, we lead this shift and help businesses to stay ahead of it. By integrating our Microbiome-Safe Scoring into product development, we provide the scientific foundation to create trusted, microbiome-friendly innovations that meet this rising demand. Our innovations are already proving that protecting the microbiome is not just better for health, but essential.
Microbiome-safe is no longer a trend. It is the foundation for the next generation of care.
